What are hallucinations and delusions?
The first thing to remember, hallucinations are usually false perceptions regarding taste, smell, and fears that do not exist. This typically occurs in elderly patients with Alzheimer’s or other forms of dementia. Trending on the same path, delusions are a false understanding of what is happening in the present. Both hallucinations, as well as delusions, occur in individuals who have dementia. Dealing with this day out and being careful not to irritate the condition any further can cause strain on you as the caregiver. Here are some great books to help you now.
How to empower caregivers with effective strategies for Hallucinations and Delusions
Empowering caregivers with effective strategies for hallucinations and delusions involves a combination of education, communication, support, and a person-centered approach. Here are some strategies that can help:
-
Educate caregivers:
Provide caregivers with information about hallucinations and delusions, including their causes, symptoms, and potential impact on individuals. Help them understand that these experiences are part of the person’s condition, not deliberate actions.
-
Foster open communication:
Encourage caregivers to establish a supportive and open dialogue with those experiencing hallucinations and delusions. Active listening and empathy are crucial in understanding their experiences and emotions.
-
Validate feelings:
Help caregivers validate the feelings and experiences of the person with hallucinations and delusions. Acknowledge their reality and emotions without trying to convince them otherwise. This validation can provide a sense of understanding and trust.
-
Maintain a calm environment:
Create a calm and structured environment for the individual, as stress and chaos can exacerbate hallucinations and delusions. Minimize noise, provide adequate lighting, and maintain a consistent daily routine to promote security.
-
Identify triggers:
Work collaboratively with caregivers to identify potential triggers for hallucinations and delusions. Certain situations, environments, or activities may increase the likelihood of these experiences. Once identified, try to minimize or avoid these triggers when possible.
-
Offer reassurance:
Teach caregivers how to offer reassurance and comfort to individuals during hallucinations or delusions. Assure them of their safety, provide a comforting presence, and avoid directly arguing or contradicting their experiences.
-
Engage in reality-oriented activities:
Encourage caregivers to engage the individual in reality-oriented activities that can help distract from hallucinations and delusions. These may include hobbies, music, gentle exercise, or other enjoyable and calming activities.
-
Maintain a consistent routine:
Establishing a consistent daily routine can provide stability and predictability for individuals with hallucinations and delusions. Consistency in mealtimes, medication schedules, and activities can help reduce anxiety and confusion.
-
Involve healthcare professionals:
Encourage caregivers to communicate regularly with healthcare professionals, including doctors, therapists, and support groups. These professionals can provide guidance, medication adjustments, and additional strategies specific to the individual’s needs.
-
Take care of caregivers’ well-being:
Caregivers play a critical role, and their well-being is essential. Please encourage them to seek support from other caregivers, join support groups, or participate in counseling services. Self-care activities, such as exercise, relaxation techniques, and taking breaks, can also help prevent caregiver burnout.
Everyone is unique, and strategies should be tailored to their specific needs and preferences. Working closely with healthcare professionals can provide further guidance and ensure a comprehensive approach to supporting individuals with hallucinations and delusions.
How to learn the journey of fear to overcome the effects of hallucinations and delusions
Learning the journey of fear and overcoming the effects of hallucinations and delusions involves a combination of self-awareness, education, therapy, and support. Here are some steps to help in this process:
-
Educate yourself:
Learn about the nature of hallucinations and delusions, their causes, and their impact on individuals. Understanding the mechanics behind these experiences can help demystify them and reduce fear.
2. Seek professional help:
Consult with healthcare professionals, such as psychiatrists or psychologists, who work with individuals experiencing hallucinations and delusions. They can provide a proper diagnosis, offer treatment options, and guide you through the journey of overcoming fear.
3. Engage in therapy:
Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be beneficial in managing fear associated with hallucinations and delusions. A therapist can help you challenge and reframe negative beliefs, develop coping strategies, and gradually confront your fears in a safe and supportive environment.
4. Build self-awareness:
Pay attention to your thoughts, emotions, and bodily sensations when experiencing fear related to hallucinations and delusions. Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, can help you become more present and aware of your reactions. This awareness can empower you to respond more effectively to your fears.
5. Challenge distorted thoughts:
Hallucinations and delusions can create distorted perceptions of reality, leading to fear and anxiety. Practice identifying and challenging these distorted thoughts. Ask yourself if there is evidence supporting your worries or if there might be alternative explanations for your experiences.
6. Develop coping strategies:
Work with your therapist to develop personalized coping strategies to manage fear and anxiety. These may include relaxation techniques, grounding exercises, distraction techniques, or engaging in enjoyable activities that promote a sense of calm and control.
7. Gradual exposure:
With the guidance of a therapist, gradually expose yourself to situations or triggers that evoke fear related to hallucinations and delusions. Start with less challenging situations and progressively work your way up, building confidence and resilience along the way.
8. Seek support:
Connect with support groups or organizations focusing on mental health or specific conditions associated with hallucinations and delusions. Sharing experiences with others who understand can provide validation, support, and inspiration for your journey.
9. Practice self-care:
Prioritize self-care activities to promote overall well-being. This includes maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, balanced nutrition, sufficient sleep, and engaging in activities that bring you joy and relaxation.
10. Celebrate progress:
Recognize and celebrate your achievements, no matter how small. Overcoming fear associated with hallucinations and delusions is gradual, and acknowledging your progress can boost your motivation and confidence.
Everyone’s journey is unique, and being patient and kind to yourself throughout the process is essential. Work closely with healthcare professionals to tailor strategies that suit your specific needs and circumstances.
Exploring Hallucinations and Delusions: Empower Caregivers with Effective Strategies
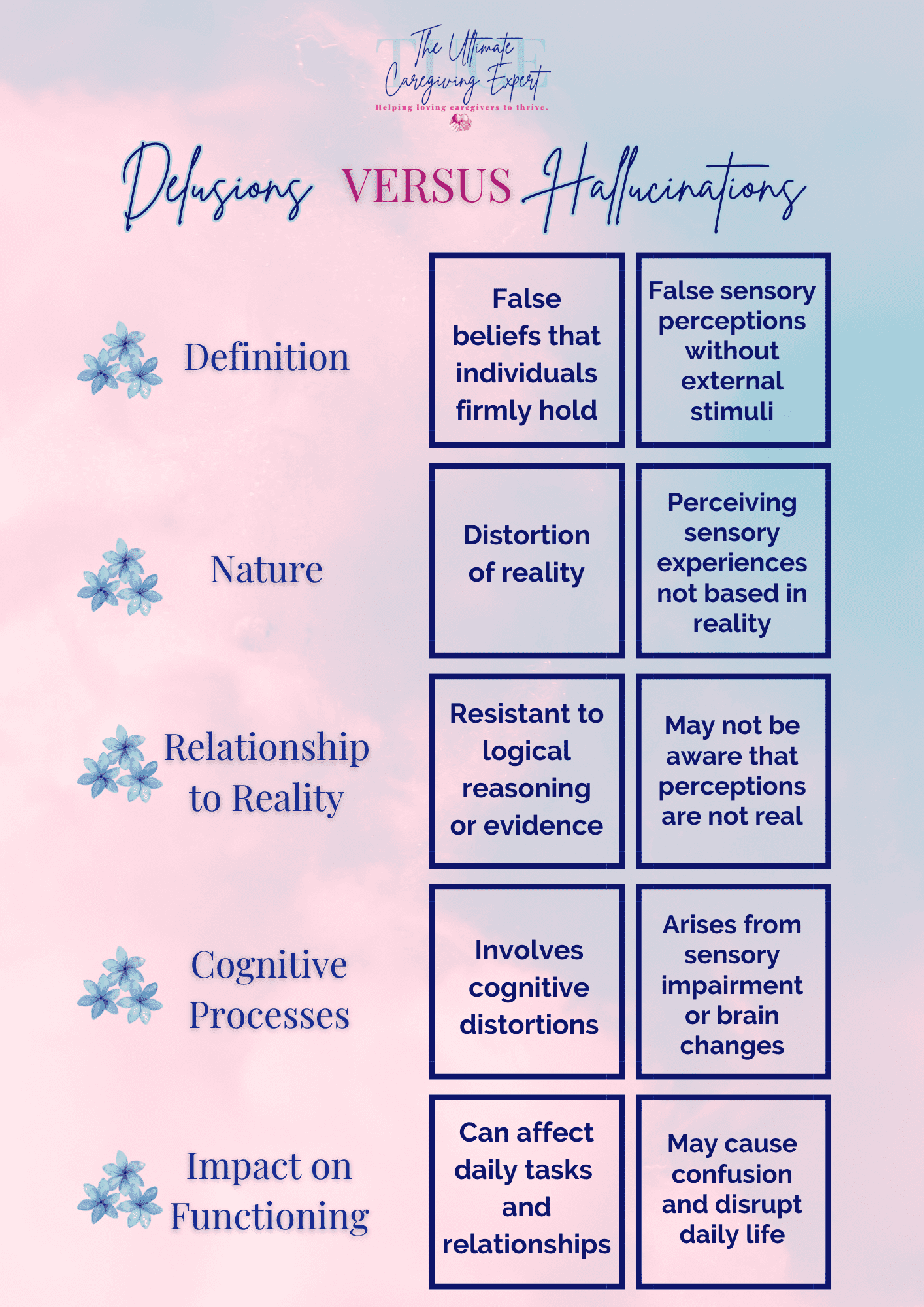
Hallucinations and delusions are two different symptoms that might be experienced by a person who has Alzheimer’s disease or another kind of dementia.
Hallucinations are a form of imaginative sensory perception in which a person imagines sensing, hearing, or tasting things that do not exist.
They might, for instance, think they feel bugs crawling on their arms or see dead relatives.
On the other hand, delusions are erroneous ideas that can lead to our loved ones living in continual terror since they may believe that other people are plotting to take from them or hurt them somehow.
Additional facts of hallucinations
Hallucinations and delusions are distinct conditions affecting our loved ones suffering from Alzheimer’s or dementia of another type. Our loved ones with hallucinations have sensory imagination. For example, they feel, hear, or taste something that does not exist. When our loved one with Alzheimer’s experiences hallucinations, they seem to feel, hear, or sense something untrue. For example, they may feel bugs crawling up on their arms and legs, see their relatives who no longer exist, and relive old experiences. All such conditions sum up hallucinations.
Additional facts of delusions
On the other hand, delusions have nothing to do with sensory experiences; but false beliefs make matters difficult for our elderly. Such a condition involves our elderly loved ones living in constant fear of something. For example, they may doubt people around them to rob them of their property or money or may even feel people or their relatives are planning to kill them.
Causes of hallucinations and delusions
Hallucinations and delusions in older people with Alzheimer’s are primarily caused due to changes in the brain. However, lenses and medication side effects can also cause our elderly to perceive false beliefs and fall prey to things or situations that are not false do not exist.
Role of Caregivers in Helping the elderly deal with Hallucinations and Delusion
Taking care of a loved one with Alzheimer’s who suffers from hallucinations and delusions is difficult. Easier said than done; caregivers have to face a lot of trouble when caring for their loved ones with an altered state of mind. However, here are some of the tips that can help all caregivers effectively deal with their elderly loved ones to help them overcome hallucinations and delusions:
- Please consult your doctor: Understanding the exact cause behind hallucinations and delusions is always necessary. Therefore, it is best to consult the doctor and take their advice about the causes and the subsequent course of treatment.
- Do not try to rationalize with your loved one: As a caregiver, you must understand that the sudden change in behavior in the form of delusions and hallucinations is not deliberate. Your seniors have no control over this and, at the same time, are unaware of their outrageous behavior. It is just impossible to rationalize with them in such cases. Trying to do so would do more harm than good and exert stress on you and your loved one. Therefore, whenever you see your seniors exhibiting their suspicions or fear regarding people or situations, it is always best to hear them out and change their focus immediately.
What should be done
In such cases, employ the 3 Rs – Reassure – Respond, and Refocus. First, reassure your loved ones that everything is fine and that you are there for them. Next, respond positively that everything will be fine and there is nothing to worry about. Finally, refocus – once you can successfully calm your senior, shift their focus to other activities or people.
Caregivers can assist in preventing or minimizing the incidence of these symptoms by gaining an awareness of the triggers, addressing the underlying issues, and cultivating an environment that is quiet and free of distractions.
Additional help with hallucinations and delusions
-
Assess the situation or the problem:
In most cases, hallucinations or delusions follow a particular pattern. So, the next time your senior experiences hallucination, determine the situation or people that triggered the specific belief or behavior. Many caregivers have the habit of recording details of such triggers to try and control the situation next time.
-
Find the actual problem:
Many hallucinations and delusions can be successfully prevented by addressing the real issue. You can try and engage your seniors in some activity requiring active participation. Moreover, hallucinations and delusions result from your seniors’ poor vision and decreased hearing ability. Therefore, regular medical checkups to keep their sensory organs working fine can also help prevent these conditions. Make surgically make your senior’s room does not have many distractions in light and loud noise, as these serve as potential factors for triggering hallucinations and delusions.
Caregiving Consulting
Caregiving can be challenging, frustrating, and highly stressful!
But it doesn’t have to be that way.
- Find peace in caregiving by tapping into resilience, joy, and radical forgiveness.
- Would you love to give care with expertise and confidence?
- Are you managing your loved one’s daily activities in an organized and structured way?
- You follow a proven caregiving system that provides for your loved one’s needs while giving you peace of mind.
I will tailor the sessions to your specific needs to:
- Explore strategies
- Determine your immediate needs by providing focus and clarity.
- Develop a wellness plan to boost your caregiving journey.
- Ensure that systems are incorporated into your caregiving journey through regular check-ins.
The Ultimate Caregiving Expert Consulting offers tools, services, and resources to give you a fresh, objective perspective on caregiving. This will help enhance your caregiving journey if you feel confined, overwhelmed, or hopeless in the role of caregiver.
Additional Education
Education in caregiving refers to acquiring the knowledge, skills, and understanding necessary to provide care for individuals who require assistance with activities of daily living, such as bathing, dressing, eating, and grooming.
This education can be obtained through formal programs or on-the-job training and experience.
Education in caregiving aims to equip individuals with the skills and knowledge necessary to provide high-quality, compassionate care for those in need.
Caregiving can be challenging, frustrating, and highly stressful!
But . . . it doesn’t have to be that way.
Imagine . . .
- Giving care with expertise and confidence
- Managing your loved one’s daily activities in an organized and structured way
- You follow a proven caregiving system that provides for your loved one’s needs while giving you peace of mind.
If the above sounds like what you need and have been searching for desperately . . . Then you need to enroll in The Ultimate Secrets to Caregiving with LESS Stress and MORE peace course!
Conclusion
It is essential to remember that the person experiencing hallucinations or delusions is not responsible for the changes in their perceptions, even though providing support to a loved one going through these experiences can be demanding.
As caregivers, we are responsible for providing reassurance, understanding, and practical guidance through effective strategies that can help the patient navigate these challenging circumstances.
By collaborating with medical professionals, implementing productive strategies, and fostering an environment of emotional and mental comfort, caregivers can make a tangible difference in the lives of those they care for.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Seek support, educate yourself about the condition, and never hesitate to seek professional assistance.
Together, we can empower caregivers and enhance the well-being of our loved ones affected by hallucinations and delusions. Check out this site.






